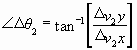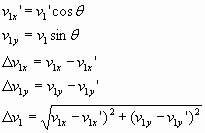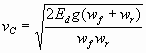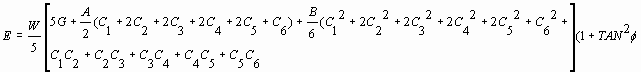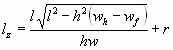|
Acceleration ft/sec/sec |
t vi ve |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acceleration Factor |
Free Fall |
|
|
|
||
|
Drag Factor |
Drag factor ¹ coefficient of friction (m ) unless on level; Add or subtract grade (G) |
Roll Resistance .01 - .02 (Free) .1 - .2 (Drive) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Velocity – Initial Vi |
t a ve |
|
|
ft/sec |
t a d |
|
|
a ve d |
|
|
|
S d f |
|
|
|
Velocity – End Ve |
t a vi |
|
|
ft/sec |
a vi d |
|
|
Velocity Average |
|
|
|
Constant Velocity - Average |
|
|
Distance d |
t a vi |
|
|
ft |
a vi ve |
|
|
t vi ve |
|
|
|
S d f |
|
|
|
Constant Velocity - Average |
|
|
|
Time |
a vi ve |
|
|
t a d When vi = 0 |
|
|
|
Constant Velocity - Average |
|
|
|
Mass |
|
|
|
Free Fall w = F |
|
|
|
Force |
|
|
Velocity
|
Fall Velocity
|
Sideslip Velocity > 10% Grade
Small Grade
Without Superelevation
|
Vault / Flip Velocity
|
|
Radius |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Lateral acceleration
|
|
Momentum
If q < 10° = Collinear
If one vehicle stopped must be collinear
If partial – Both must be in same direction
Vehicle 1 must be on x axis & vector tails must be at origin (direction) for angle determination
|
|
|
|
Collinear |
Collinear |
|
|
|
If same post collision velocity If same post collision velocity
|
|
|
Determine velocity for vehicle #2 first, then use in equation for #1
|
|
|
|
|
|
PDOF = ΔV PDOF Angle = |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Soh Cah Tah |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Component Method For 90º Only
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
John Daily |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
PDOF #1 α 1 =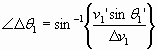 |
PDOF #2 α 2 =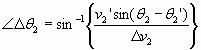 |
|
|
Approach angle V2
|
|
ACTAR Study Guide |
|
|
Establish weight ratio between vehicles w1=1, w2=w2 /w1 Determine post impact speeds If vehicle 1 on east/west axis 0 – 180 then Solve for S1 If vehicle 2 on north/south axis 90 – 270 then
Solve for S2 |
Δv= Speed & direction at impact Speed & direction post impact Break post impact movement into components for example west (x axis) & south (y axis)
Δv west= Pre impact speed east/west axis +/- post impact speed on east/west axis Δv south = Pre impact speed north/south axis +/- post impact speed on north/south axis
or |
|
Δv must be inverse and proportional |
Component System
or
|
|
IPTM α = Alpha PDOF or approach angle V1θ = Theta departure angle V 1′ψ = Psi approach angle V 2Φ =Phi departure angle V 2′ |
V1 = v1 =Vehicle #1 approach speed (S) or v V2 = v2 =Vehicle #2 approach speed (S) or v V3 = v1′ =Vehicle #1 departure speed (S) or v V4 = v2′ =Vehicle #2 departure speed (S) or v |
Energy
|
Sliding Energy
|
Kinetic Energy
|
Velocity
|
|
|
Potential Energy Pe = mgh |
|||
|
|
|
||
Velocities For Same Direction Collision
|
Closing
|
Rear Vehicle
|
Front Vehicle
|
Energy From Crush
Two Measurements
|
|
Four Measurements
|
|
Six Measurements
|
|
||
|
E=Energy dissipated in-lbs |
A=maximum force w/o permanent damage |
|
|
W= Width of crush region inches |
B=Spring stiffness per inch damage lbs/inch |
|
Center of Mass
|
Longitudinal
|
Vertical
|
Resultant Drag Factor
|
|
|
Drag Factor With Side Slip
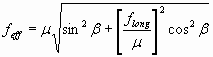
Velocity From Gear Position
|
|
v = 0.00436RD |
|
D = drive wheel/tire diameter (inches) |
IMPT
|
Conversion Factors
|
1.467(mph) = ft/sec |
|
|
|
Impulse = Ft = Δmv = ΔP = lbs-sec |
||
Newton #1 A body will remain at rest or in constant motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force
Newton #2 ![]() a) Describes what happens
when force is applied b) quantifies force in magnitude and direction
a) Describes what happens
when force is applied b) quantifies force in magnitude and direction
Newton #3 ![]() Forces are equal and
opposite
Forces are equal and
opposite
Quadratic Equation Where![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
|
Law of Pythagoras
|
|
|
Send mail to madpi@smn.com with
questions or comments about this web site.
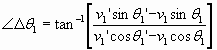
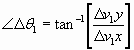 or
or